
Ultrasound Phantom
About[]

Whole Body Phantom Kyoto Kagaku PBU-50
A phantom is used to control the imaging performance of ultrasound transducers. The spatial resolution, dead zone, linear fidelity, depth of penetration and image uniformity is important for the image quality. Ultrasound phantoms are generally of two types. One mimics the acoustic properties of tissue (with regard to the speed of sound, average attenuation, etc.). The main purpose of the other is to approximate the sonographic appearance of tissue. The latter is often used as a biopsy training aid. Those which mimic the acoustic properties of tissue have been constructed of agar with suspended graphite,’ polyurethane foam,2 and magnesium silicate gels,3 and are used chiefly as test phantoms for assessing diagnostic ultrasound imaging equipment or for studying the interaction of sound with tissue. The "whole body phantoms" are life-size, full body anthropomorphic phantoms with a state-of-the-art synthetic skeleton, lungs, liver, mediastinum and kidneys embedded in a soft tissue substitute. Movable joints allow basic positioning for plain X-ray and training/research applications that can be enriched by disassembling the phantom into 10 individual parts (head, limbs and trunk). Typical tests may include horizontal and vertical distance accuracy as well as depth of penetration measurements comparing all sets of mix and match error or values obtained with the same transducer and set frequency ranges.
Quality Assurance Testing[]
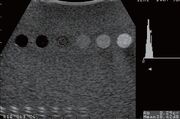
QA image using a phantom. The center mass cylinders represents contrast and the bottom cylinders represent depth markers.
Ultrasound Quality Assurance (QA) testing can be very useful both for daily assessment and further research. Gray scale for contrast evaluation, cyst targets with non-resonance cylinders, line targets for geometrical evaluation, close range (dead zone) resolution, axial and angular resolution are prepared for probe scanning. Probe performance can be evaluated at various depths and can be up to 200 mm depth depending on phantom model. QA tests support hospital accreditation requirements through an ultrasound Quality Assurance testing program directed by a hospital physician or medical physicist. The same tests must be performed during each testing period so that changes can be monitored over time and effective corrective action can be taken. Testing results, corrective action, and the effects of corrective action must be documented and the documentation maintained on site (radiology department). [1]
Manufacturers[]
Links[]
References[]
Video[]
thumb|300px|right|Quality Assurance of Medical Ultrasound Systems - Segment One